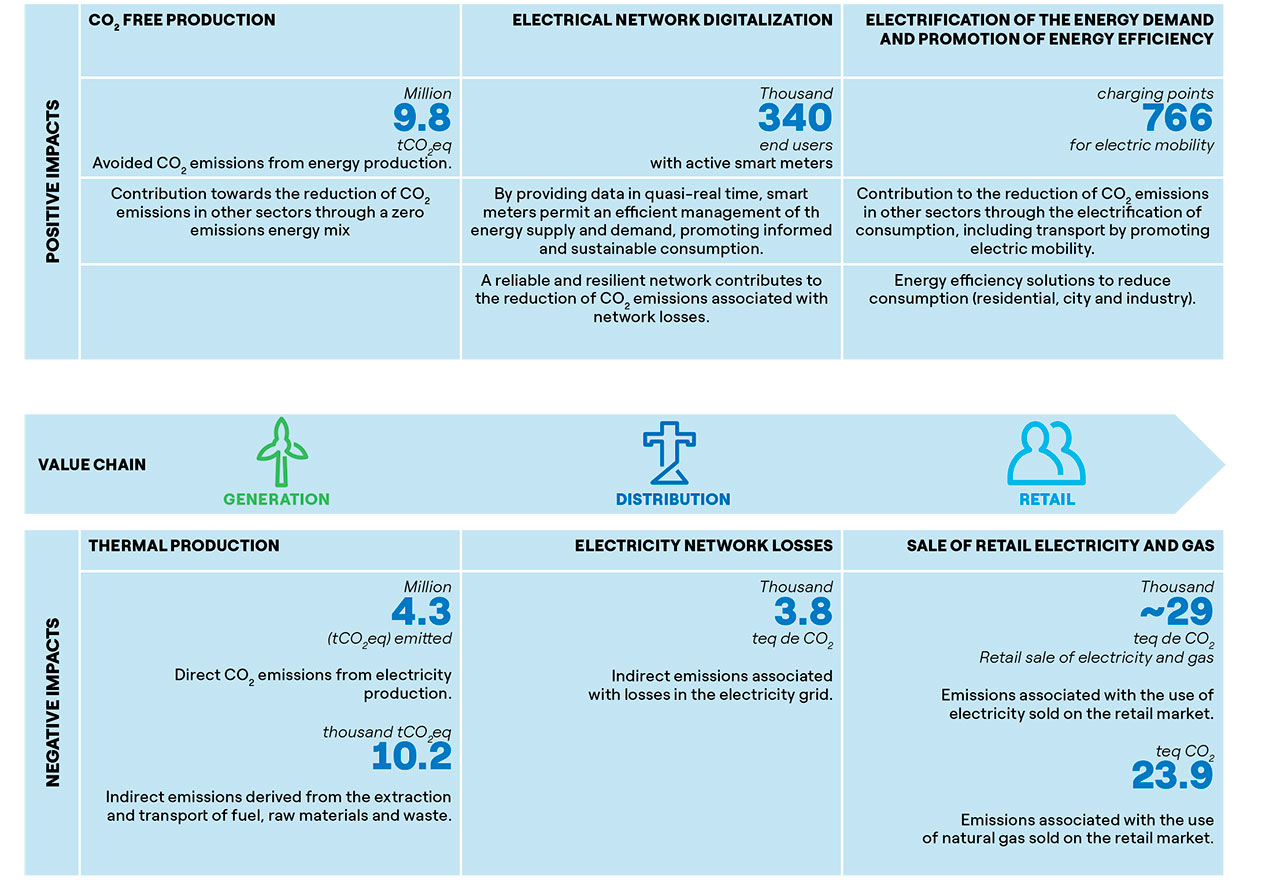
Enel Chile' impacts on climate change in 2020
(*) The Atacama-Taltal Gas Pipeline operates at low capacity (roughly 4% of its capacity) and without a compressor, which has reduced gas leaks to zero (0%) over the last 3 years.
Strategy to tackle climate change
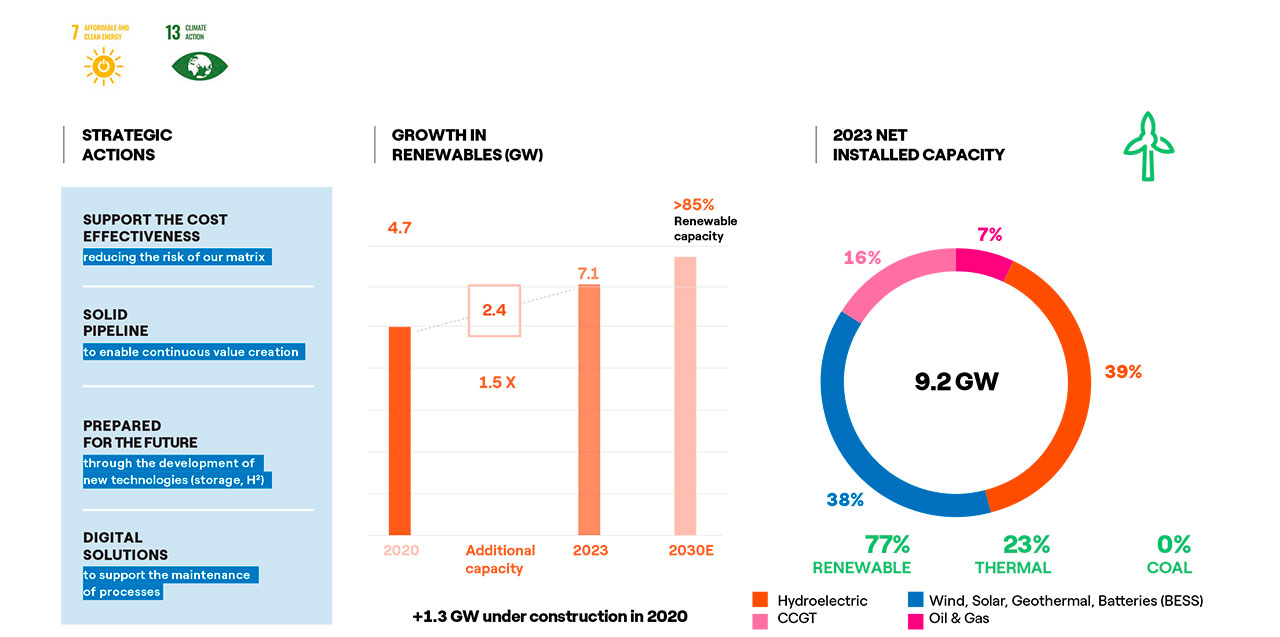
The sustainability strategy developed in recent years and the integrated business model have allowed Enel Chile to create value for all its stakeholders, seizing the opportunities that emerge from the energy transition and from climate action. To this end, the Company has so far focused its actions on decarbonization with the concrete action of closing coal-fired power plants, and through investments aimed at increasing renewable energy capacity, enabling network infrastructures and implementing platform models, taking full advantage of technological and digital evolution, which will favor electrification and the development of new services for customers. The actions are aimed at contributing in an accelerated manner to the objectives that slow down the impacts generated by global warming in accordance with the Paris Agreement. In this context, the strategic plan presented in December 2020 places at the center of the corporate strategy the acceleration of the energy transition hand in hand with sustainable growth, creating shared and significant value for shareholders, customers, the company and the environment.
The strategic plan calls for investments of US$ 2.4 billion, 70% of which will be allocated to the renewable energy business, mainly to increase its generation capacity. With these investments, 77% of Enel Chile’s generation will be produced by renewable resources by 2023, and it is expected to exceed 85% by 2030.
Greenhouse gas emissions reduction targets
As a result of this strategy and analysis, Enel Chile set its reduction goals for direct emissions by 2023.
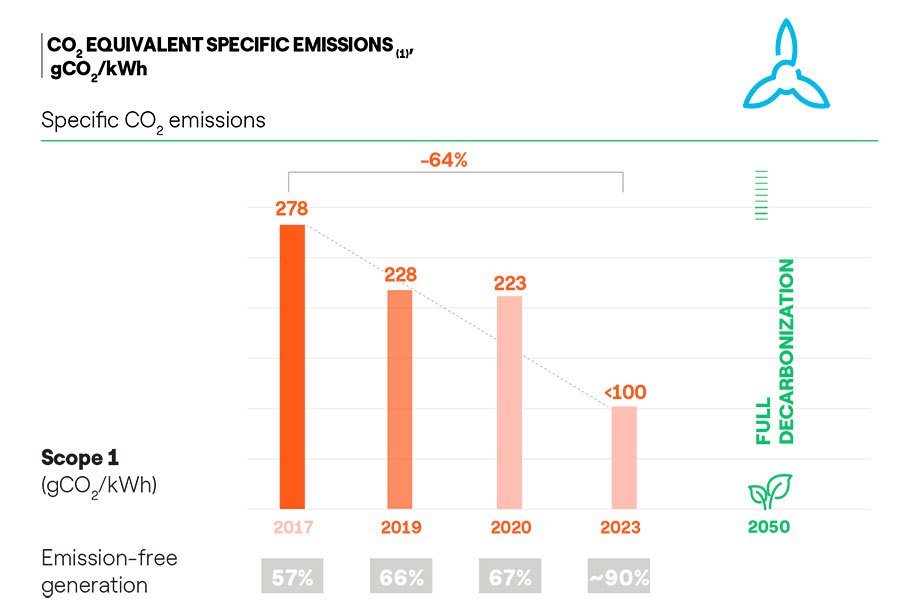
For the Scope 1 Total Emissions Inventory, according to the GHG Protocol standard and in line with the Science Based Target initiative, emissions from Thermal Power Plants are considered at 99% and other emissions at 1%. The latter emissions include inventories associated with the auxiliary services of production and distribution plants, vehicles under the Company’s control, as well as emissions from fossil fuel combustion in boilers and office cafeterias.


